Written by: Segun Akomolafe
5G represents the fifth generation of cellular network technology, designed to connect virtually everyone and everything—including machines, objects, and devices. Unlike previous generations, 5G was built to deliver unprecedented speeds, minimal latency, and massive capacity.
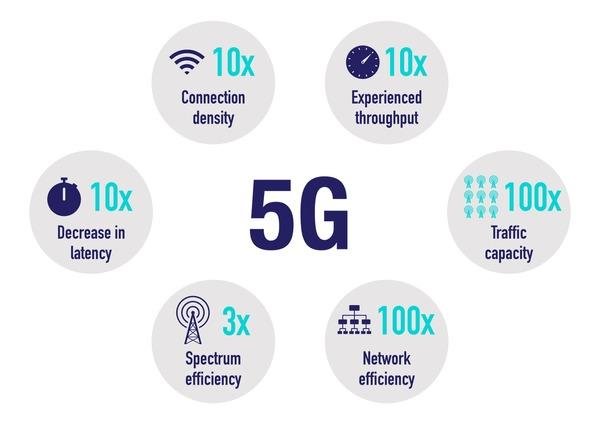
When you hear about 5G, you’re hearing about a technology that’s not just an incremental improvement over 4G. It’s a fundamental redesign of how wireless networks operate, providing speeds up to 100 times faster than 4G while supporting a million devices per square kilometer—far beyond what previous networks could handle.
“Overview of 5G network”
How 5G Works
5G operates across multiple frequency bands, each with distinct characteristics:
- Low-band spectrum (600-700 MHz): Provides wide coverage but relatively modest speed improvements over 4G
- Mid-band spectrum (2.5-3.7 GHz): Balances coverage and capacity with speeds between 100-900 Mbps
- High-band spectrum (millimeter waves, 24-47 GHz): Delivers multi-gigabit speeds but with limited range and poor obstacle penetration
The technology uses smaller cells with advanced antenna technologies like Massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) systems that employ dozens of antennas on a single array. This enables more focused beams of data to specific users, improving efficiency dramatically.
5G networks also employ network slicing—creating multiple virtual networks within a single physical network infrastructure—allowing operators to dedicate portions of their network to specific use cases with different requirements.
Read more: Top 5 Electric Scooters for Urban Commuters
5G Vs. 4G Vs. 3G
The following table shows the differences become 5G and other previous generation networks, such as 4G and 3G:
| Features | 3G | 4G | 5G |
|---|---|---|---|
| Download Speed | Up to 2 Mbps | Up to 100 Mbps | Up to 10 Gbps |
| Latency | 100 – 500 ms | 30 – 50 ms | 1 – 10 ms |
| Connection Density | Low | Medium | Very high |
| Battery Efficiency | Low | Medium | High |
The practical implications are significant. Your 4G connection might let you download a full HD movie in about 10 minutes, while 5G can complete the same task in seconds. The ultra-low latency makes real-time applications like autonomous vehicles and remote surgery possible, as the network responds almost instantaneously to commands.
Benefits of 5G Networks
5G’s advantages extend far beyond faster downloads on your smartphone. Some other benefits include:
Enhanced Mobile Broadband
You’ll experience dramatically faster data speeds—up to 10 Gbps under ideal conditions. This means buffer-free 4K streaming, instant downloads, and seamless cloud access. Virtual and augmented reality applications become truly mobile, opening new entertainment and education possibilities.
Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications
With latency as low as 1 millisecond, 5G enables applications requiring near-instantaneous response times. This makes possible:
- Autonomous vehicles that can communicate with drivers and other vehicles in real-time
- Remote surgery where surgeons can operate robotic instruments from thousands of miles away
- Industrial automation with precise real-time control over machinery
Massive Machine-Type Communications
5G networks can support up to 1 million connected devices per square kilometer, enabling true Internet of Things (IoT) deployment at scale. Your smart home devices, wearables, and sensors can all maintain reliable connections simultaneously without network congestion.
Potential Applications and Use Cases
“Applications of 5G network”
5G will transform numerous industries through the following improvements:
Healthcare
Telemedicine will evolve beyond video consultations to include remote patient monitoring with real-time data transmission from wearable devices. Surgeons can perform operations from different locations using haptic feedback equipment that transmits touch sensations with imperceptible delay.
Transportation and Automotive
Connected and autonomous vehicles will communicate with each other and infrastructure to improve safety and traffic flow. Your car will receive real-time updates about road conditions, accidents ahead, and optimal routes based on current traffic patterns.
Smart Cities
Urban infrastructure will become more efficient through connected utilities, traffic systems, and public services. Smart lighting systems will adjust based on pedestrian and vehicle traffic, while waste management systems will optimize collection routes based on fill levels of smart bins.
Entertainment and Media
Immersive technologies like VR and AR will become truly mobile. You’ll be able to participate in live events remotely with 360-degree video streams, or collaborate with colleagues in virtual spaces that feel physically present.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its great benefits, 5G faces the following significant obstacles:
Infrastructure Requirements
The dense network of small cells required for millimeter wave deployment means massive infrastructure investment. Hundreds of thousands of new cell sites are needed nationwide, each requiring fiber backhaul connections and permission for installation.
Coverage Issues
High-frequency signals face physical limitations—they don’t travel far and can be blocked by buildings, trees, and even rain. This means dense urban areas will see the fastest deployment, while rural areas may wait years for meaningful 5G coverage.
Health and Safety Concerns
While scientific consensus indicates 5G is safe, public concerns persist about potential health effects from increased radio frequency exposure. The World Health Organization and numerous scientific bodies have found no evidence of health risks from 5G networks operating within established safety guidelines.
Security Vulnerabilities
The expanded network surface area creates more potential entry points for cyber attacks. Network slicing and the massive IoT ecosystem introduce new security challenges that require robust encryption and authentication protocols.
Read more: Top 5 Electric Bikes for Commuting
Global 5G Deployment Status
The 5G rollout varies significantly by region. Some countries are yet to adopt the network into their communication system because they don’t yet have the required infrastructure. Here are the deployment status of 5G network in various regions:
North America
The United States has led commercial deployment, with major carriers offering 5G services in dozens of cities. However, coverage remains spotty, with mmWave deployments limited to dense urban cores and broader coverage using lower-band spectrum with less dramatic speed improvements.
Asia-Pacific
South Korea, China, and Japan lead in 5G deployment. South Korea achieved over 10 million 5G subscribers within 18 months of launch. China has installed hundreds of thousands of 5G base stations, more than the rest of the world combined.
Europe
European deployment has progressed steadily but faced regulatory hurdles and spectrum allocation delays. Countries like Switzerland, the UK, Germany, and Spain have commercial 5G networks, though widespread coverage remains a work in progress.
Developing Nations
Many developing nations are in early planning stages, focusing on ensuring 4G coverage before investing heavily in 5G. The digital divide risks widening as advanced economies move to 5G while others struggle with basic connectivity.
Future of 5G and Beyond
5G will continue evolving through the following standardization updates:
5G Advanced
Expected in 3GPP Release 18 and beyond, 5G Advanced will bring enhanced capabilities for industrial IoT, improved positioning accuracy, and better power efficiency. These improvements will make industrial applications more reliable and extend battery life for IoT devices.
6G on the Horizon
Though still conceptual, 6G research has begun with potential commercial deployment in the 2030s. Early research suggests terahertz frequencies, sub-millisecond latency, and integrated intelligence throughout the network. Your future devices may leverage AI at the network level rather than solely on the device.
Read more: Top 10 Most Affordable Electric Vehicles
How to Prepare for 5G
To make the most of 5G as it becomes available, check for 5G compatibility across multiple bands. Not all 5G phones support mmWave, which delivers the fastest speeds. Consider your usage patterns—if you primarily use your phone at home with Wi-Fi, immediate 5G adoption may not be necessary.
However, as a business owner, begin by assessing potential 5G applications for your industry. Develop projects that could leverage high bandwidth or low latency. Consider how IoT deployment could improve operations, and begin developing necessary skill sets among IT staff.
 “5G network infographic”
“5G network infographic”
Conclusion
5G represents more than just faster phones—it’s a fundamental shift in what’s possible with wireless technology. The full impact will emerge gradually as infrastructure expands and innovative applications develop.
Whether you’re a consumer excited about lightning-fast downloads or a business leader exploring new operational possibilities, understanding 5G’s capabilities and limitations helps you make informed decisions about when and how to adopt this transformative technology.
As with previous generations, the most revolutionary applications may be ones we haven’t yet imagined. The combination of massive connectivity, ultra-low latency, and high bandwidth creates a platform for innovation that will reshape industries and daily life in the coming decade.
Other Valuable Contents:
